Fire valves for oil heating | From 1.5 to 30m in length - oil tank valve
Post-filtration uses a carbon filter to remove any remaining tastes or odours. This final step ensures the water is crisp and clean.
Lead is a toxic metal that can enter drinking water through old pipes and plumbing systems. Exposure to lead can cause serious health problems. RO systems effectively remove lead, providing safe drinking water.
Reverse osmosis is a highly effective water purification technology that provides numerous benefits. It removes a wide range of contaminants, improves the taste and odour of water, and supports overall health by providing clean and safe drinking water. RO systems are versatile, suitable for residential, commercial, and specialised applications, making them an excellent choice for anyone seeking high-quality water filtration.
Yes, reverse osmosis water is safe to drink. It is free from harmful contaminants, making it a reliable source of clean drinking water.
Periodic cleaning and sanitising of the RO system are necessary to prevent the buildup of contaminants and ensure the longevity of the system. Regular maintenance ensures the system continues to provide high-quality water.
PRVvalve
Scaling occurs when dissolved minerals precipitate and form deposits on the RO membrane. This can be prevented by using antiscalant chemicals, ensuring proper pre-treatment of the water, and maintaining the correct water chemistry.
Clean water is essential for good health. RO systems provide water free from harmful contaminants, helping to prevent waterborne diseases and reduce exposure to harmful chemicals.
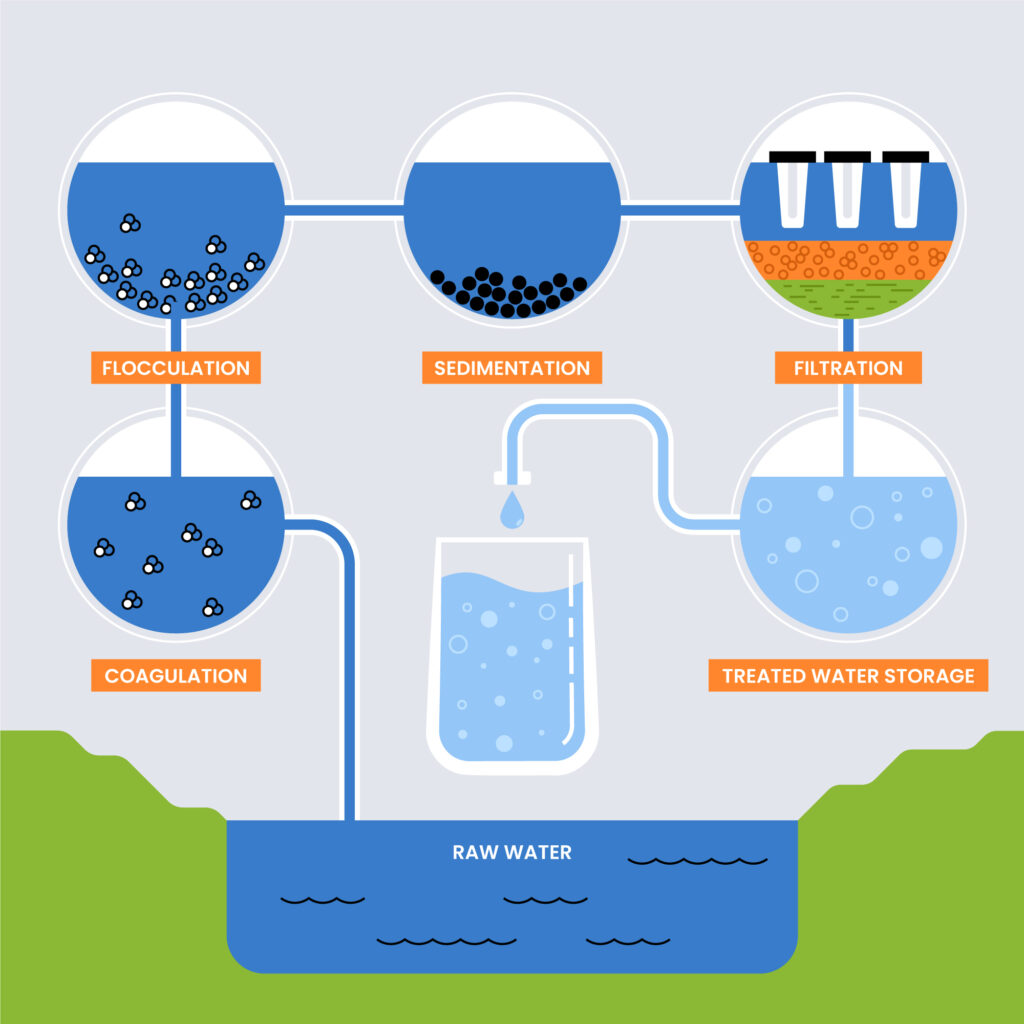
Osmosis is the natural movement of water through a semi-permeable membrane from low to high solute concentration. Reverse osmosis reverses this process by applying pressure to force water through the membrane, leaving contaminants behind. This results in purified water on one side and a concentrated solution of contaminants on the other. This is the fundamental principle of how RO works.
Fluoride is commonly added to municipal water supplies to prevent tooth decay. However, excessive fluoride can be harmful. RO systems effectively remove fluoride, ensuring safe levels for consumption. Research from the CDC on water treatment supports this.
Chlorine is used to disinfect water and kill harmful microorganisms. However, it can cause unpleasant tastes and odours. RO systems remove chlorine, improving the taste and safety of drinking water.
Regulatingvalve
When choosing a reverse osmosis system, consider your specific water quality needs, budget, and maintenance requirements. Research and select a reliable system that offers the best performance and efficiency. Regular maintenance and sustainable practices will ensure your RO system continues to provide the highest quality water for years to come.
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a water purification technology. It uses a semi-permeable membrane to remove ions, molecules, and larger particles from drinking water. This process effectively removes many types of dissolved and suspended species, including bacteria. RO is used in both industrial processes and potable water production. Understanding the reverse osmosis process is essential for grasping its benefits.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep a reverse osmosis system functioning effectively. This includes replacing filters and membranes at recommended intervals. Pre-filters should be replaced every 6-12 months, while the RO membrane may last 2-3 years depending on water quality and usage. The Australian Government Department of Health emphasises the importance of regular maintenance to ensure water safety.
Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that can contaminate groundwater. Long-term exposure to arsenic can lead to serious health issues. RO systems remove arsenic from water, reducing the risk of exposure.
UV purification uses ultraviolet light to kill bacteria and viruses but does not remove dissolved contaminants or improve taste and odour. Reverse osmosis, on the other hand, removes both biological and chemical impurities, providing a more complete solution for water purification.
Water quality is crucial for health. Reverse osmosis (RO) technology ensures that the water we drink is free from harmful contaminants. This guide explains what reverse osmosis is, how it works, its benefits, and its applications.
Reverse osmosis is essential for providing safe drinking water. It removes contaminants harmful to health. Research from the WHO on drinking-water quality shows that RO can remove heavy metals, chemicals, and microorganisms. This makes it reliable for both residential and industrial use.
WFC Water Flow Control Pty LtdABN 85 059 365 49037/317-321 Woodpark Rd, Smithfield NSW 2164P 02 9948 0699info@waterflowcontrol.com.au
Pressureregulator
Distillation involves boiling water and condensing the steam to remove impurities. While effective, it is energy-intensive and slower compared to reverse osmosis. RO systems provide a more efficient and faster method of water purification.
Biofouling, the accumulation of microorganisms on the RO membrane, can reduce the efficiency of the system. This can be managed through regular cleaning, using biocides, and maintaining proper pre-treatment of the water to reduce the load of microorganisms.
In homes, RO systems provide safe drinking water. They can be installed under the kitchen sink or as whole-house systems, ensuring that every tap and appliance has access to purified water. RO systems improve the taste and quality of drinking water and protect household appliances from scale buildup.
Carbon filtration removes chlorine, organic compounds, and improves taste and odour. However, it does not remove dissolved salts, heavy metals, or microorganisms. Reverse osmosis provides a more comprehensive filtration solution by removing a wider range of contaminants.
Implementing sustainable practices can help reduce the environmental impact of reverse osmosis. These practices include using energy-efficient systems, recycling wastewater, and regularly maintaining the system to ensure it operates at peak efficiency. Advances in technology continue to improve the sustainability of RO systems, making them more eco-friendly.
Pre-filtration uses sediment and carbon filters to remove larger particles and chlorine. Sediment filters capture physical debris like sand and rust. Carbon filters remove chlorine and organic compounds that cause bad taste and odours. This stage protects the RO membrane and enhances system efficiency.
RO systems significantly improve water taste and odour by removing chlorine and other impurities. This results in water that is not only safe but also enjoyable to drink.
Waterpressureregulator
RO systems are used in specialised applications where water quality is critical. In aquariums, RO systems provide clean water that supports the health of aquatic life. In restaurants, purified water enhances the flavour of food and beverages. RO systems are also used in laboratories and healthcare facilities.
Watervalve
Pre-filters should typically be replaced every 6-12 months, while the reverse osmosis membrane may last 2-3 years depending on the quality of the incoming water and the system’s usage.
The RO membrane allows water molecules to pass through while blocking contaminants. This ensures that only clean, purified water reaches the other side. Understanding the reverse osmosis membrane is key to knowing how RO systems work.
Reverse osmosis systems do not remove dissolved gases like carbon dioxide and some small organic molecules. Additional filtration methods may be required to remove these specific contaminants.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) are harmful chemicals found in industrial and consumer products. RO systems remove these contaminants, providing cleaner and safer water.
One of the criticisms of reverse osmosis systems is water waste. Traditional RO systems can produce a significant amount of wastewater. However, modern systems are designed to be more efficient, reducing the amount of wastewater produced. Some systems also incorporate recycling features to minimise waste. The United States Environmental Protection Agency discusses these improvements.
Slow water flow in an RO system can be caused by clogged filters, low water pressure, or a fouled membrane. Regular maintenance, including replacing filters and checking for clogs, can help address this issue. Ensuring the system operates at the correct water pressure is also crucial for optimal performance.
RO is widely used in commercial and industrial settings. Industries such as pharmaceuticals, food production, and electronics manufacturing require high-purity water for their processes. RO systems ensure product consistency and safety. In restaurants and hotels, RO improves the taste and quality of water used in cooking and beverages.




 8615510865705
8615510865705 
 8615510865705
8615510865705