How to Adjust Your Water Pressure Regulator - pressure regulator valve
All cell lines were validated for H3 K27M expression by Western blot and Sanger sequencing using the following primer sequences: H3F3A K27M (forward sequence: 5′-GTT TGG TAG TTG CAT ATG GTG ATT-3′; reverse sequence: 5′-ACA AGA GAG ACT TTG TCC CAT T-3′) and HIST1H3B K27M (forward sequence: 5′-GGG CAG GAG CCT CTC TTA AT-3′; reverse sequence: 5′-ACC AAG TAG GCC TCA CAA GC-3′) every 3 months, and all cell lines were validated by STR DNA fingerprinting annually as well as mycoplasma testing every 3 months.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock icon ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
MR images to track orthotopic tumor development were obtained using a Bruker Avance 300 MHz (7T) vertical bore nuclear MR spectrometer (Bruker Biospin). Animals were placed under isoflurane anesthesia, and 3D T2-weighted fast spin echo sequences were acquired with the following parameters: TE 45.20 msec, TR 2000 msec, bandwidth 110 kHz. The total imaging time per mouse was approximately 10 minutes per scan. Animal core temperatures were maintained at 37°C by a warm airflow.
The authors report no conflict of interest concerning the materials or methods used in this study or the findings specified in this paper.
FBV Inc. | 1563 Your Engineered Solutions for Industrial Valves | FBV Inc. is an ISO 9001 certified company specializing in ...
H3 K27–altered diffuse midline gliomas (DMGs) are frequently biopsied to obtain tissue diagnosis, inform clinical decision-making, and determine clinical trial eligibility. Tissue yield from biopsies is typically low, leaving little material available for research. To advance understanding of disease biology and promote preclinical testing of novel therapeutics, collecting viable cellular material from treatment-naive tumors is of paramount importance. Here, the authors report the feasibility of a practicable technique for creating DMG cell lines and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) without the need for additional biopsy specimens. Tumor cells are obtained by probe washing immediately after completion of biopsy. Wash fluid is collected, and viable cells are expanded in vitro. Cultured cells are used to establish PDX rodent models. A total of 5 patient samples were collected by this technique. Viable tumor cells were obtained from 3 of the 5 samples, and cell lines suitable for experiments were obtained within 6–8 months. Orthotopic implantation and flank engraftment was successful in 1 of the 3 established cell lines. Animals harboring intracranial tumors were euthanized due to disease burden 6–7 months after stereotactic injection. Flank tumors formed within 4–5 months and were serially passaged. Molecular and tissue analyses confirmed retention of H3 K27M expression and loss of H3 K27me3 in all cell lines and PDXs.
All animals orthotopically engrafted with primary tumor cells developed intracranial tumors. Again, BLI demonstrated progressive tumor burden over time with an exponential growth rate (Fig. 4C). Brain MRI was additionally performed to track orthotopic tumor development. T2 sequences revealed large hyperintense, expansive, and infiltrative lesions situated in the ventral pons and pontomesencephalic junction of the mouse brain (Fig. 4D). Orthotopically xenografted mice reached a moribund state 6–7 months after tumor cell injection, which is in line with previously reported intracranial DMG xenografts.15,19 Molecular and tissue analysis again confirmed H3 K27M expression and loss of H3 K27me3 (Fig. 4E).
Low Flow, Low Pressure Regulators ... Two NEW valves have been added to Jordan Valves Low Flow range. Although aimed primarily at the Gas Regulator market, they ...
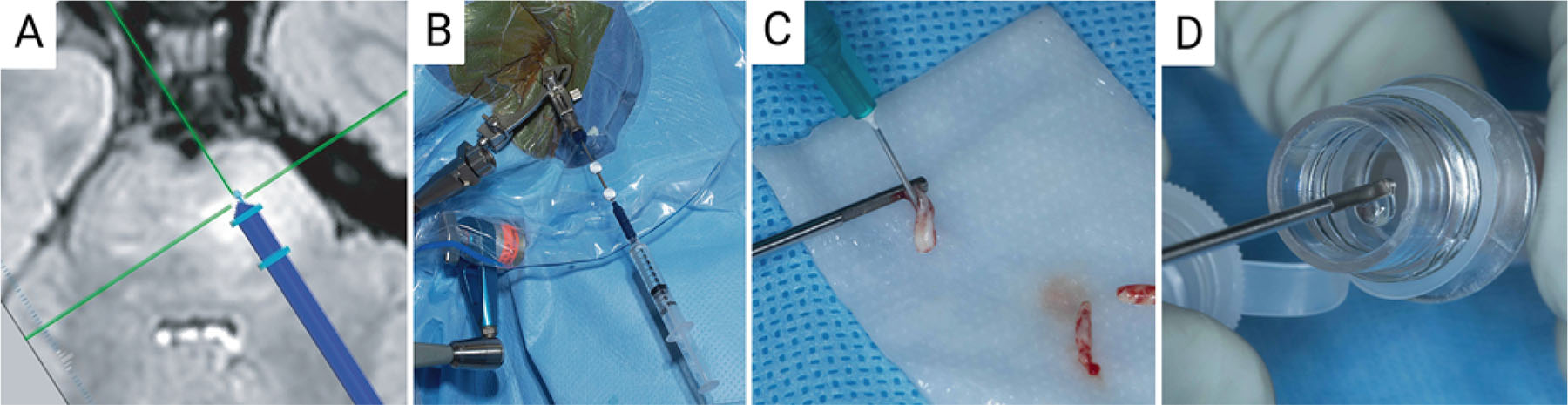
Percutaneous biopsy and needle wash acquisition. A: MRI-guided planning showing the catheter trajectory for completing a stereotactic biopsy in the pons. B: Stereotactic setup in the operating room. C: Tissue obtained from the needle biopsy. D: Probe washing after biopsy without visible tumor within the probe. Created with BioRender.com. Figure is available in color online only.
All cell lines were initially identified and ultimately authenticated by DNA fingerprinting using short tandem repeat (STR) analysis and tested for mycoplasma every 3–6 months. Sanger sequencing for detection of histone H3 gene mutations was performed over the same interval. Cells were validated for H3 K27M–mutant histone expression and loss of trimethylation of histone H3 K27 (H3 K27me3) by Western blotting as previously described.17,18
Check valve
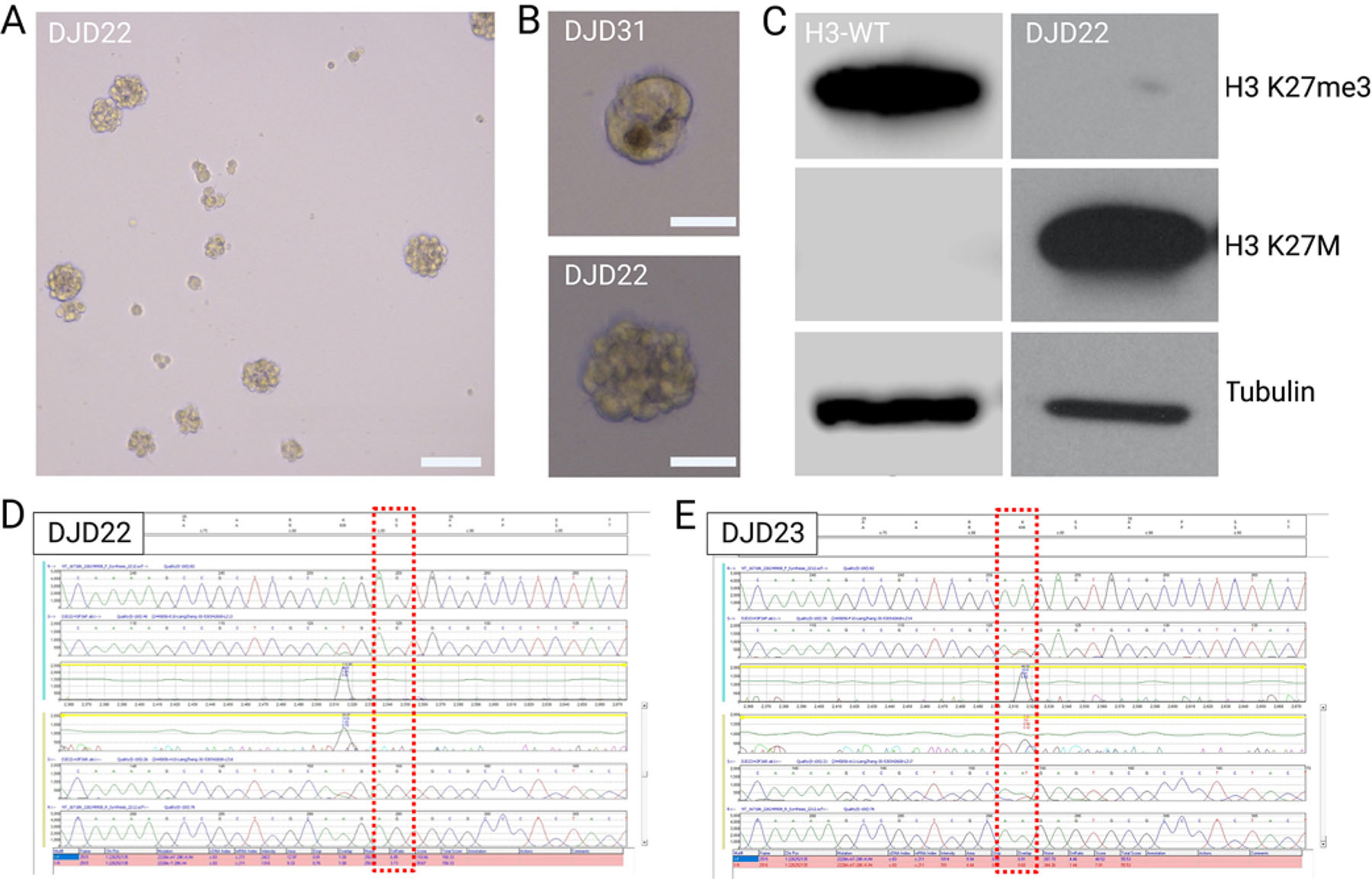
In vitro expansion and cell line development. A: Images of a developing neurosphere cell line. Original magnification ×5 (bar = 100 μm). B: Single neurospheres of the DJD22 and DJD31 cell lines. Original magnification ×20 (bars = 50 μm). C: Western blot of DJD22, demonstrating high levels of H3 K27M with a loss of H3 K27me3. D and E: Sanger sequencing of DJD22 (D) and DJD23 (E) cell lines highlighting H3 gene mutations on the H3F3A allele. WT = wild type. Created with BioRender.com. Figure is available in color online only.
Conception and design: Daniels, Rechberger, Zhang. Acquisition of data: Rechberger, Zhang, Ge, Nesvick, Miller. Analysis and interpretation of data: Daniels, Rechberger, Zhang, Nesvick. Drafting the article: Daniels, Rechberger, Zhang. Critically revising the article: Daniels, Zhang, Nesvick. Reviewed submitted version of manuscript: Daniels, Rechberger, Zhang, Ge, Nesvick. Approved the final version of the manuscript on behalf of all authors: Daniels. Statistical analysis: Rechberger. Administrative/technical/material support: Rechberger. Study supervision: Daniels, Nesvick.
Parts of this work were presented in a poster presentation at the AANS/CNS Joint Section on Pediatric Neurological Surgery 2022 Annual Meeting, Washington, DC, December 1–4, 2022.
Historically, surgeons and oncologists alike were reluctant to biopsy DMG for concerns regarding procedure-associated morbidity and the lack of actionable therapeutic alterations following tissue diagnosis.6,7 This severely limited tissue availability for research, thus limiting the development of preclinical models for drug and hypothesis testing. More recently, multiple groups have demonstrated that these tumors may be biopsied with acceptable morbidity risk.8–12 Together with a resurgence in postmortem tissue collection, the increasing availability of previously scarce tumor specimens has proved critical for seminal biological and therapeutic investigations.13,14
Animals were monitored daily and euthanized by CO2 inhalation when symptomatic. Flank tumors and brains were harvested for molecular analysis by STR, Sanger sequencing, and Western blotting as detailed above. Additionally, the maintenance of H3 K27M expression and loss of H3 K27me3 were histopathologically assessed. Formalin-fixed tissue specimens were embedded in paraffin and sectioned in the coronal plane (5 μm/section) using a microtome (CM1860 UV, Leica Biosystems). H&E staining was performed according to standard protocol. For immunohistochemical analysis, tissue sections were dewaxed in xylene and rehydrated in ethanol. Antigen retrieval was performed by steaming slides in a citrate buffer (10 mM trisodium citrate, 0.05% Tween 20, pH 6.0). Sections were blocked with 10% normal goat serum in 1× Tris-buffered saline for 30 minutes at room temperature. Primary antibodies (H3 K27M [catalog no. 190631] at a 1:500 dilution, Abcam; H3 K27me3 [catalog no. 9733S] at 1:100, Cell Signaling) were diluted in Tris-buffered saline with 2% normal goat serum and 0.5% Triton X-100. A VECTASTAIN Elite ABC kit (Vector Laboratories) containing biotinylated secondary antibodies was applied according to the manufacturer’s instructions, and slides were developed with SignalStain DAB Substrate Kit (Cell Signaling) for visualization. Sections were counterstained with hematoxylin and mounted with Permount (Thermo Fisher Scientific). Images were acquired using a digital slide scanner (Axio Scan.Z1, Carl Zeiss Microscopy).
For both professionals and DIY enthusiasts, maintaining optimal water pressure is crucial to ensuring a well-functioning plumbing system.
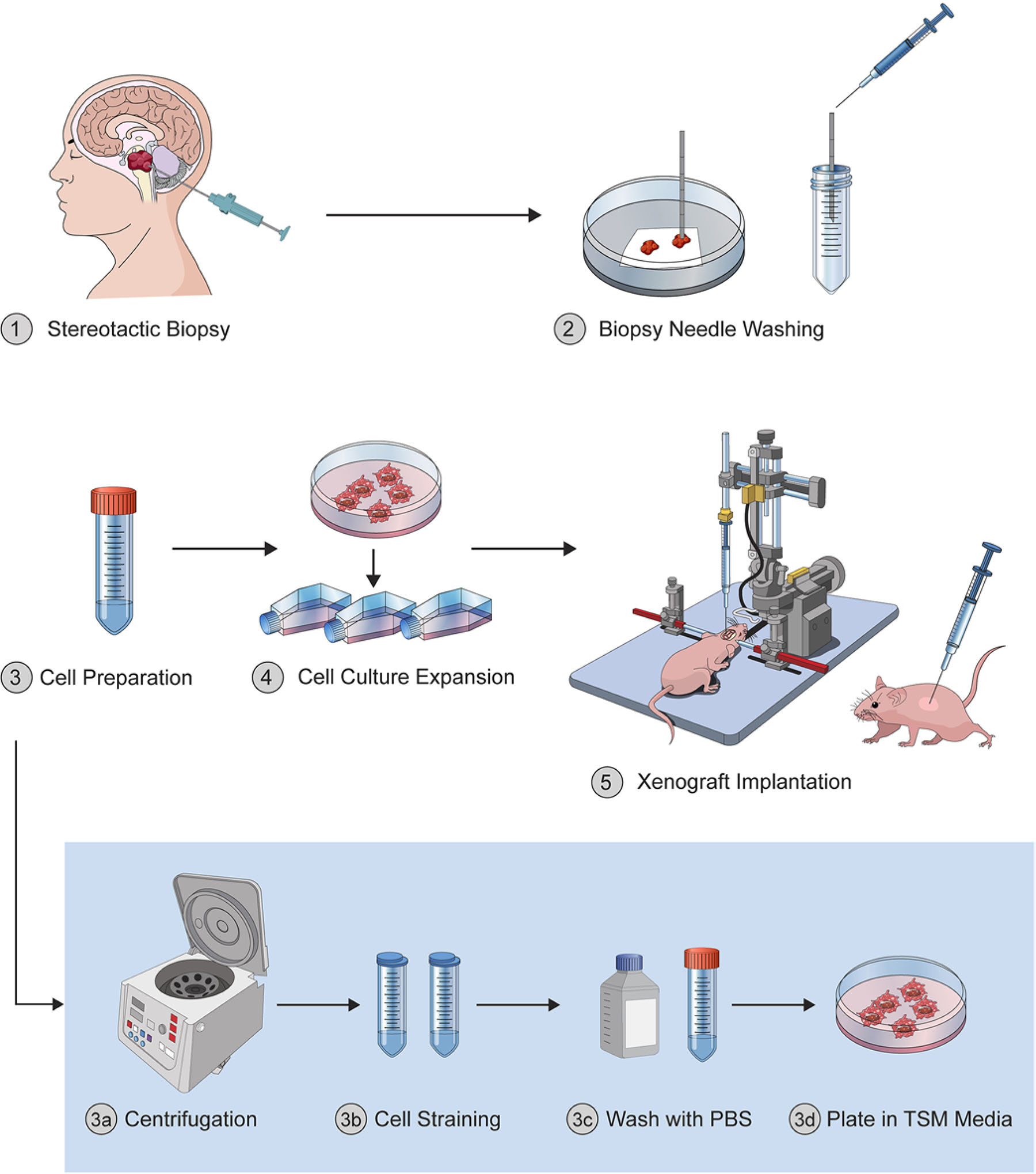
The workflow for the protocol described is illustrated in Fig. 1. Patients were placed in a lateral decubitus position and placed in Mayfield pinion fixation with the biopsy site facing upward. After registering with the frameless stereotactic system (StealthStation, Medtronic) and ensuring excellent anatomical accuracy (< 1-mm predicted trajectory error), a target was chosen and the entry site planned to facilitate a trajectory perpendicular to bone that avoided all major scalp, emissary, cortical veins, and sulci. A small amount of hair was clipped over the biopsy entry site, which was then prepped with iodine and draped in the usual sterile fashion.
Subcutaneous and intracranial tumor engraftment using cultured cells was performed as previously described.17–19 Briefly, to establish flank xenografts, tumor cells were resuspended in a single-cell suspension of 1:1 Matrigel (Corning) and sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) (Thermo Fisher Scientific) solution at 500,000 cells/μL. Six- to 7-week-old athymic nude mice (Hsd:athymic Nude Foxn1nu, Charles River Laboratories) subsequently received a subcutaneous injection of 2,000,000 cells (200 μL) into the soft tissue flank. Orthotopic xenografts were generated by injecting 500,000 cells placed in single-cell suspension in 5 μl of sterile PBS (Thermo Fisher Scientific) through a 0.5-mm burr hole 2 mm lateral and 1 mm caudal to the lambda. The injection depth was 4.2 mm. Using a 26-gauge (51-mm, point style AS) syringe (Hamilton), cells were administered stereotactically at a constant rate of 0.5 μl/min into the pons of athymic nude mice (6–7 weeks old; Charles River Laboratories).
In vivo engraftment of DJD22 cells. A: BLI demonstrating subcutaneous tumor development in the flank of Hsd:athymic Nude Foxn1nu mice. B: Visible flank tumor approximately 4 months after engraftment. The insets show histopathological and immunohistochemical staining of disease-characteristic markers. Original magnification ×20 (bars = 50 μm). C: Tumor volume of orthotopically engrafted cells shown by BLI. D: Coronal T2-weighted MR images showing a large hyperintense, expansive, and infiltrative tumor situated in the ventral pons and pontomesencephalic junction of the mouse brain. E: Representative H&E-stained and immunohistochemical-stained (H3 K27M, H3 K27me3) images of formalin-fixed intracranial tumor sections. Original magnification ×20 (bars = 50 μm). ROI = region of interest. Created with BioRender.com. Figure is available in color online only.
HF Scientific, 16260 Airport Park Drive Fort Myers, FL 33913 United States, (484) 619-5238, Business Category: Plumbing & Water.
Globe valve
BLI indicated that the take rate of tumor cells in the flank was approximately 60%–80%, with visible tumor formation becoming apparent within 4–5 months after engraftment (Fig. 4A). Tissue collected from subcutaneous PDX tumors was analyzed on a regular basis and demonstrated the retained H3 K27M expression and loss of H3 K27me3 (Fig. 4B). Preliminary flank grafts from one cell line (DJD22) have been serially passaged with a flank tumor generation time of approximately 2 months.
H3 K27–altered diffuse midline glioma (DMG) is a uniformly lethal primary brain tumor diagnosed in approximately 300 children per year in the United States.1 Because of its diffusely infiltrative growth pattern and critical location in the brainstem, resection is not feasible.2 The clinical standard of care remains fractionated radiation therapy with an overall dose of 54–59 Gy, which facilitates transient symptom improvement but does not slow disease progression or improve overall survival.3 Numerous clinical trials have failed to show any survival benefit, and patients usually die of disease within 12–15 months of diagnosis.4,5
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Viable cellular material was obtained from biopsy probe washes in 3 of the 5 cases. The average time for tumor cells to begin exponentially proliferating in the flask was approximately 3 months after the initiation of cell culture. Viable cell lines were fully formed within 6–9 months of biopsy. Two cell lines survived further passaging (DJD22 and DJD31). Established cultures grew as neurospheres with a doubling time of approximately 48–72 hours (Table 1, Fig. 3A and B). Western blot analysis demonstrated expression of an H3 K27M protein as well as limited expression of H3 K27me3 (Fig. 3C). STR and Sanger sequencing confirmed cell line identity as well as patient-specific H3F3A gene mutations (DJD22 and DJD23) (Fig. 3D and E).
We thank Mr. Ryan Meloche from the Mayo Clinic Metabolomics Core for helping us with obtaining MR images. Figures 2–4 were created with BioRender.com.
Gate valve
Informed consent in compliance with institutional review board approval at the Mayo Clinic was obtained for all human tissue studies. Detailed information regarding the origin of tumor samples, molecular status, and other pertinent data can be found in Table 1.
Solenoid valve
The lack of clinical progress against DMG necessitates a better understanding of the underlying disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic vulnerabilities of these tumors.4,16 In this study, we demonstrate the feasibility of a novel procedural technique to generate treatment-naive biopsy-derived DMG models with minimal added patient risk. Probe washing after stereotactic needle biopsy allows for collecting viable DMG cells that can be processed for cell line development and in vivo tumor formation. The proposed technique provides an easy-to-implement strategy for obtaining previously untreated tumor samples for research purposes without wasting precious biopsy material or exposing patients to additional procedure-related risk.
A cross-connection is any actual or potential connection between a potable (drinking) water system and any source of pollution or contamination.
A tekmar control system adds value to any building by improving the efficiency and durability of the HVAC system while increasing the comfort and quality.
Established cell lines were successfully transduced with a lentiviral luciferase reporter system, which allowed for repeated bioluminescence readout to monitor progress of flank and orthotopic tumor development via BLI. The identity of cells transduced with the fluorescent protein labels was regularly confirmed.
Illustration of the experimental workflow. Procedural steps for establishing cell lines and xenograft models from probe washing after stereotactic needle biopsy of DMG, H3 K27 altered. © Julian S. Rechberger, published with permission. Figure is available in color online only.
In vivo tumor progression was monitored by bioluminescence imaging (BLI) using an IVIS-200 Imaging System (Xenogen Corp.). Animals were dosed with a 10-mg/kg intraperitoneal injection of luciferase substrate (CycLuc1, Glixx Laboratories) and imaged 10 minutes thereafter under isoflurane anesthesia. Quantification of total flux (photons/sec) within regions of interest was performed using LivingImage 4.3 (PerkinElmer).
During the course of the study, 5 patients with radio-graphically diagnosed pontine DMG underwent biopsy via percutaneous stereotaxy (Fig. 2). The cohort included 3 females and 2 males, with a median age at diagnosis of 11 years. Two of the 5 patients died within the 1st year of diagnosis (1 patient died 17 months after the biopsy and 2 patients are still alive 7 and 14 months after treatment initiation). In all biopsy samples, the radiographic diagnosis of H3 K27–altered DMG was histopathologically confirmed by expression of an H3 K27M protein and loss of H3 K27me3 by immunohistochemical analysis (Table 1).20
ballvalve中文
The Pure Water San Diego Program will use proven water purification technology to clean recycled water to produce safe, high-quality drinking water. The Program ...
SunTouch electric snow melting systems make it easier to enjoy winter. Our ProMelt line of mats, cables, contactors, and controls are designed for fast ...
Biopsy wash samples were placed on dry ice immediately after surgical acquisition. Samples were centrifuged at 500g for 3 minutes to pellet tumor cells, and the supernatant was gently aspirated. Tissue was gently reconstituted in tumor stem cell medium (TSM), composed of DMEM/F12 (Life Technologies) supplemented with Neurobasal (-A) (Life Technologies) and B-27 (-A) media supplements (Life Technologies), as well as 4 μg/mL heparin (Sigma Aldrich), 20 ng/mL human EGF (Pepro-Tech US), 20 ng/mL human b-FGF (PeproTech US), 20 ng/mL human PDGF-AA, and 20 ng/mL human PDGF-BB (Shenandoah Biotechnology). Cells were subsequently filtered through a 40-μm cell strainer (CELLTREAT Scientific Products), washed again with TSM, and centrifuged. Cells were resuspended in TSM and placed in a vented T25 cell culture flask (Corning) and maintained at 37°C, 5% CO2 with incubator humidification. After 7–14 days, half the media volume was refreshed every 7–10 days. Fully formed neurospheres were passaged into new T25 flasks containing 10–15 mL of fresh TSM every 2–3 weeks, depending on the proliferation rate of each individual cell line.
Multiple preclinical models for DMG exist, and more are in the pipeline as our knowledge of DMG etiology expands.21 The increased availability of human tissue samples and genetically engineered mouse models (GEMMs) has provided valuable insights into DMG biology and promise to improve therapy. Patient-derived cell lines and PDXs have the benefit of most accurately reflecting the human disease.22 Unfortunately, they are relatively rare, in part due to a historic reluctance to surgically obtain tissue from DMG patients.15,23–25 Tissue derived from autopsy has previously yielded valuable material for research but is likely altered by treatment, including additional mutations, metabolic changes, and selected tumor sub-populations.26–28 While autopsy specimens may serve as a valuable tool to delineate changes occurring in DMG in response to therapy, these limitations demand an improved patient-derived model for future work that more accurately reflects the treatment-naive and -derived tumor and surrounding milieu. GEMMs are an important complement to PDXs as they possess an undisturbed tumor microenvironment and an intact blood-brain barrier in the context of immune-proficient animals.21,29,30 However, most GEMMs are not exclusive to the pons region of the brainstem, and the cell-of-origin and driver mutations used in different studies limit translatability to the human disease.31–34 The different types of preclinical DMG models complement each other, and a combination of approaches is needed to facilitate a better understanding of the disease and allow for the development of efficacious therapeutics.
Butterfly valve
All animal experiments were conducted in accordance with the Mayo Clinic Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee–approved protocol. Established cell lines were labeled via transduction with a pRRLSIN-18.PPT. LUC-GFP.pre lentiviral vector (a gift from Dr. Michelle Monje, Stanford University), followed by enrichment of transduced cells with stable integration and authentication with STR, Sanger sequencing, and Western blotting as described above.14,19
Using the Stealth Vertek precision aiming device and serial reducing tubes (Medtronic), a drill with a premeasured drill stop (Stryker Corp.) was used to puncture the skin and drill an access hole through the full thickness of the skull. A Bugby wire was then used to cauterize the underlying dura and pia maters, and a premeasured navigated biopsy needle was gently passed to depth. Four serial biopsies were taken circumferentially, and after each specimen was extracted, the needle was irrigated with 5 mL sterile saline, which was saved for cell harvesting. The biopsy stylet was copiously irrigated between biopsies to ensure that no bleeding was observed. Following the final biopsy, the needle was gently removed and the wound was closed with a figure-of-eight 4–0 Monocryl suture.
Tissue yield from image-guided stereotactic needle biopsies is low, leaving little material for research purposes.15 The majority of DMG laboratory models are either obtained at autopsy from heavily pretreated patients or genetically engineered animals, limiting their clinical validity. Research into the genetic, epigenetic, and immune landscape of previously untreated human DMG is of paramount importance to develop novel molecular diagnostics and treatment strategies for this devastating disease.16
Cleveland, OH · Toledo, OH · Chicago, IL · Springfield, MO · Dayton, OH · Columbus, OH · Nashville, TN · Louisville, KY. CALL. Phone: (866) 986-6860. Call for ...
The data shown here demonstrate that wash fluid from biopsy probes can be used for the development of DMG cell and xenograft models without the requirement of a separate surgical procedure; however, this study has several limitations. First, the number and diversity of tumor cells obtained by this method are inherently limited by the quantity of cells adherent to the stereotactic needle and likely recapitulate only a small subset of the entire disease biology. We recognize that cell and xenograft models only represent a subpopulation of the overall tumor. Moreover, as cell lines and xenografts are passaged, additional mutations are gained or inherited and we do not know how that affects studies performed with these models.35 Importantly, however, key disease-specific markers required for WHO CNS5 (fifth edition of the WHO classification of tumors of the CNS) diagnosis were retained throughout the model generation. Second, glioma cells are known to be exceedingly fragile ex vivo, and ongoing efforts in our laboratory are aimed at optimizing cell procurement and culture to improve survival of collected cells and better capture intratumoral heterogeneity that exists in DMG. Third, it is our experience that treatment-naive DMG cells are indolent in culture and grow slowly in animals initially. Serial passaging of flank xenografts can expedite the turnaround rate but comes with the risk of genetic drift in patient-derived tumor cells, which can give rise to malignant murine tumors that do not resemble the human disease.35
Here, we set out to test the technical feasibility of creating treatment-naive patient-derived cell lines and patient-derived xenografts (PDXs) of DMG specimens obtained from otherwise discarded biopsy probes without visible tumor samples within the probe. This may yield viable tissue for research without the need for additional biopsy specimens.
Our water closet carriers are used to reinforce the support of wall-hung toilets at home or on your worksite. We also carry in-wall toilet tanks that don't ...
Here, we demonstrate the feasibility of probe washing after stereotactic needle biopsy to collect viable DMG cells for cell line development and both flank and orthotopic PDX tumor formation. The main advantage of this approach is the fairly straightforward methodology at minimized additional risk to the patient, which facilitates procurement of untreated tumor samples and thus the development of treatment-naive disease models of DMG.




 8615510865705
8615510865705 
 8615510865705
8615510865705