Plastic Y-Strainer Filter with Stainless Steel Filter Screen - stainless y strainer
Calculatevelocityinpipefrom pressure
The irregular motion and increased mixing of fluid particles in turbulent flow lead to higher energy dissipation and pressure losses.
Saves time by providing quick and easy calculations, eliminating the need to perform complex mathematical calculations manually.
Gravitypipeflowcalculator
In contrast to laminar flow, where fluid particles move in parallel layers, turbulent flow rate involves eddies, vortices, and mixing of fluid particles.
Several factors, including friction between the fluid and the interior surface of the pipe, the presence of fittings and valves, and other losses, cause this decrease in pressure.
In general, the pressure drop is determined by multiplying the fluid velocity, the fluid density, and the head loss, which is the equivalent of the pressure drop in terms of the height of the fluid.
Pipeflowvelocity
Calculate velocity through a pipe quickly and easily, eliminating the need to perform complex mathematical calculations manually.
The pipe roughness and pipe length (pipe l) will result in a higher pressure drop, while the opposite will result in a lower pressure drop.
These parameters are used in calculating pressure drop, and the specific values will depend on the specific conditions of each piping system.
As the Reynolds number (Re) exceeds 2000, the transition from laminar to turbulent flow occurs, marking a point where pressure drop calculations become more complex.
Gasvelocityinpipe Calculator
Pressure drop calculations are crucial for ensuring efficient operation and preventing damage to equipment. Whether you're dealing with laminar or turbulent flow, our online calculator provides accurate results.

User-friendly and requires no special training or technical knowledge. Just provide the input and receive detailed results.
A more viscous and higher-velocity (flow rate) fluid will result in a higher pressure drop, while the opposite will result in a lower pressure drop.
The amount of pressure (in psi) lost per foot of pipe depends on several factors, including the pipe diameter (pipe d), the pipe roughness interior surface, the velocity of the fluid flowing through the pipe, the flow rate, and the density of the fluid.
It can be calculated using fluid dynamics principles, and the specific equation used will depend on the conditions of the piping system.
There is no set value for pressure loss per foot of pipe, as it varies based on the specific conditions of each piping system.
Sewerpipe velocity Calculator
There's a reason we are rated 4.9/5 for customer support on Capterra. Our integrated help button means that a real engineer will assist with any design query, no matter how big or small.
With advancements in technology, pressure drop calculations have become much easier with a pressure drop online calculator.
As the calculation can be measured in terms of ft/second and m/second, there are two different calculation methods to establish pressure drop:
Pipe velocity
It looks like you're using an ad blocker. We get it, but (1) terrylove.com can't live without ads, and (2) ad blockers can cause issues with videos and comments. If you'd like to support the site, please allow ads.
It's important to note that the above formula is a simplified version of the pressure drop equation, and there may be other losses (such as fittings, valves, etc.) that need to be considered when calculating the total in a piping system.
Pipe velocity Calculatormetric
Whether you're a seasoned professional or just starting, this guide will give you a comprehensive understanding of pressure drop, its calculations, and how our online calculator can help.
Pipe VelocityChart
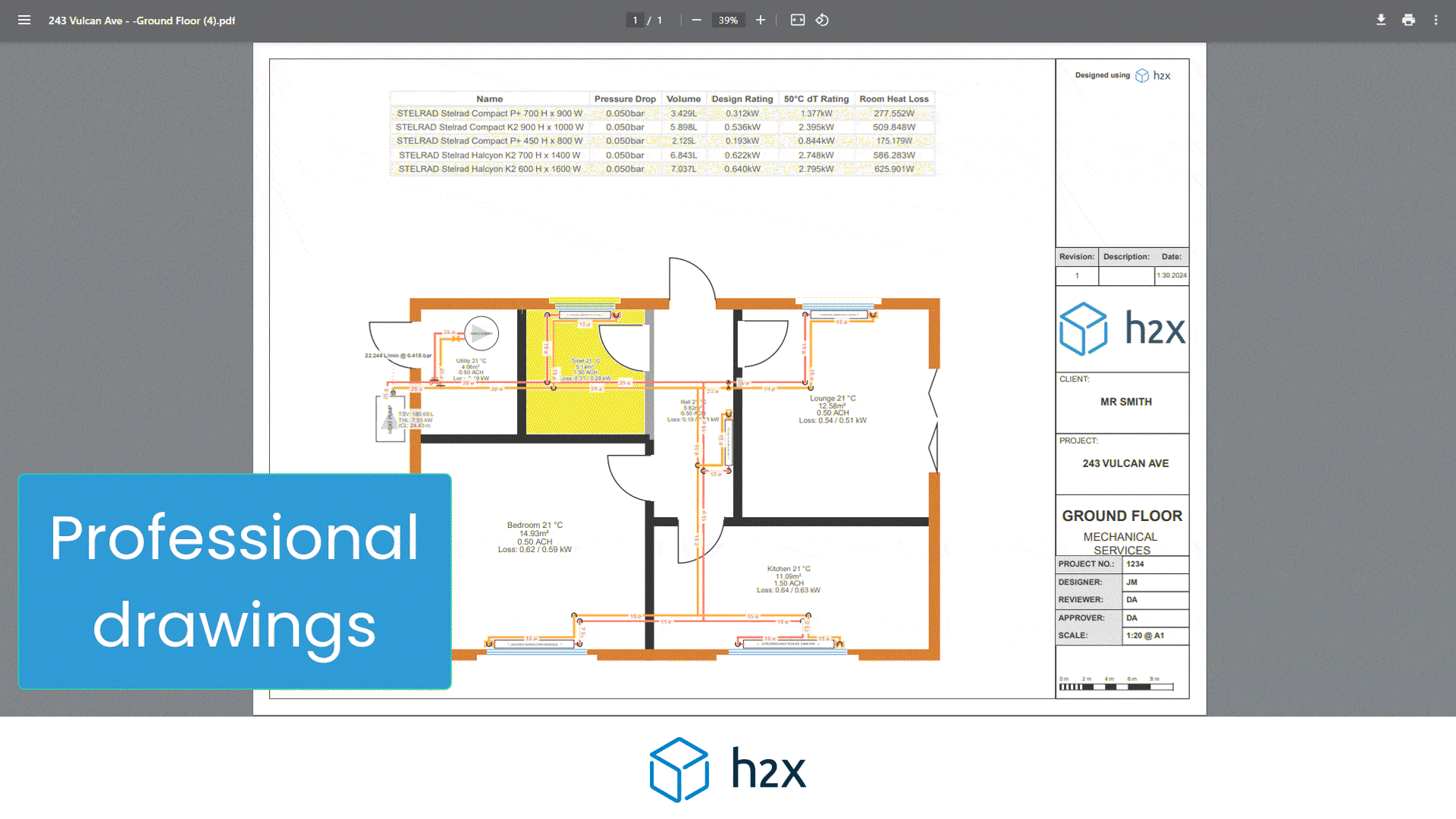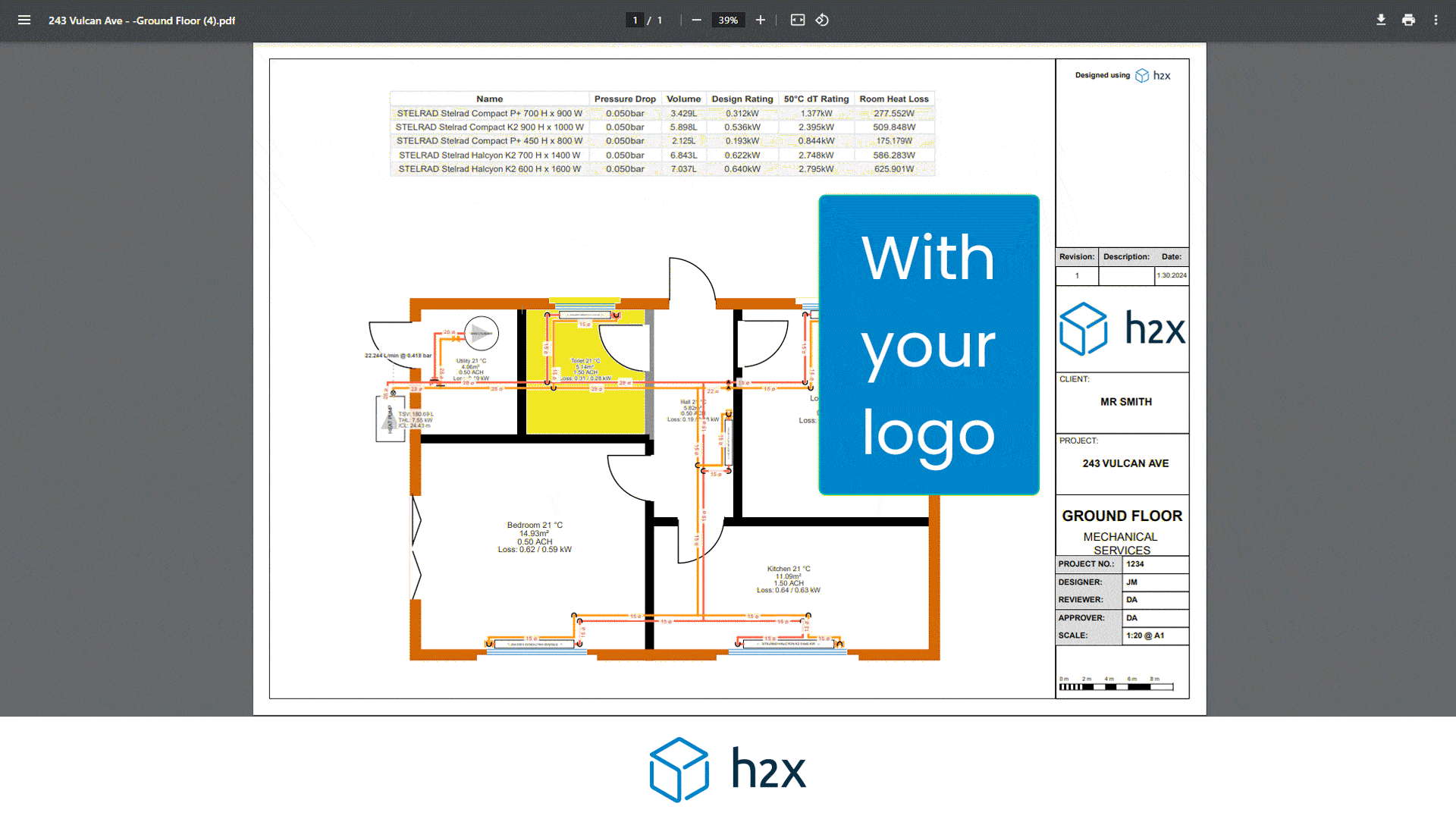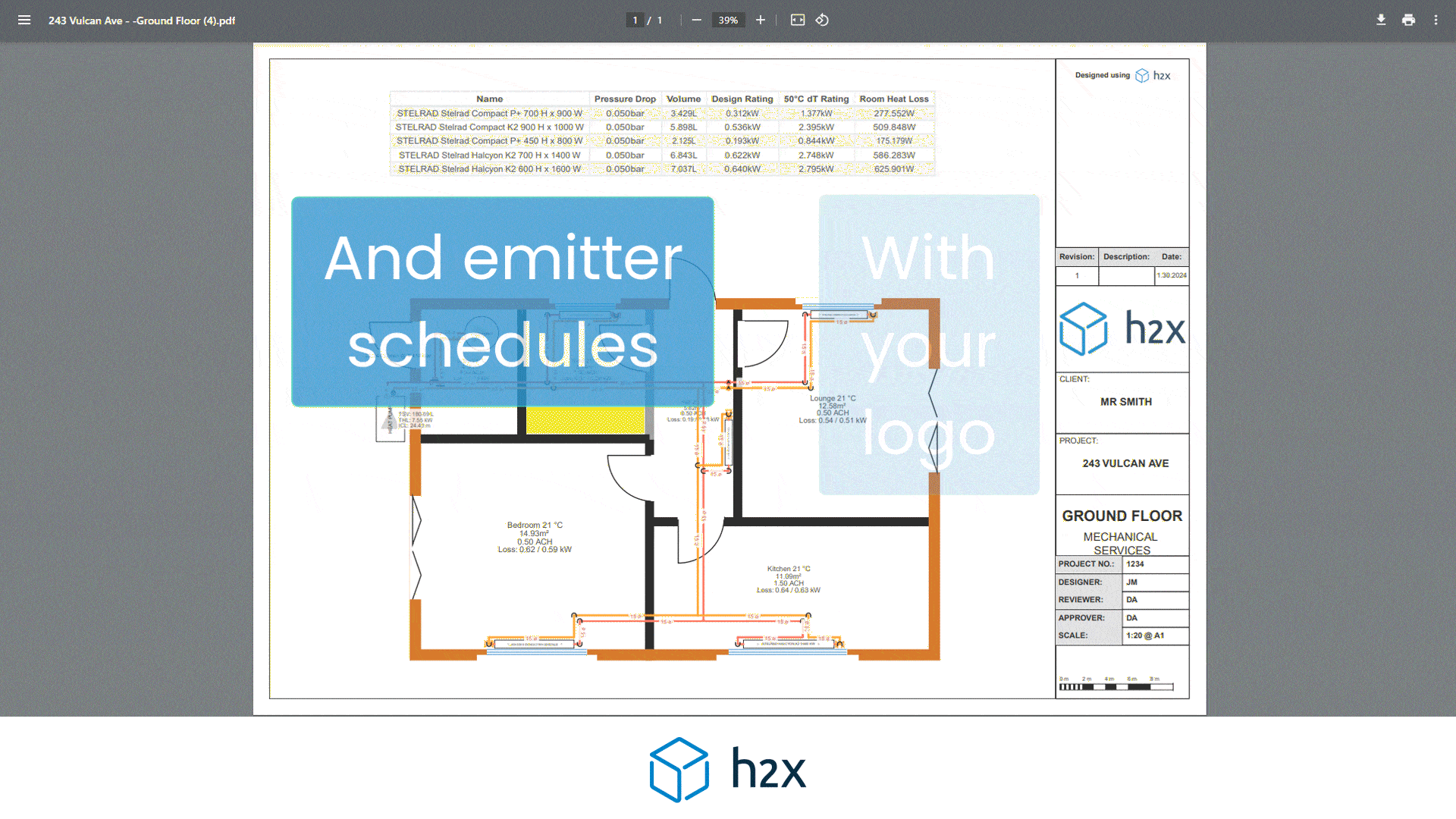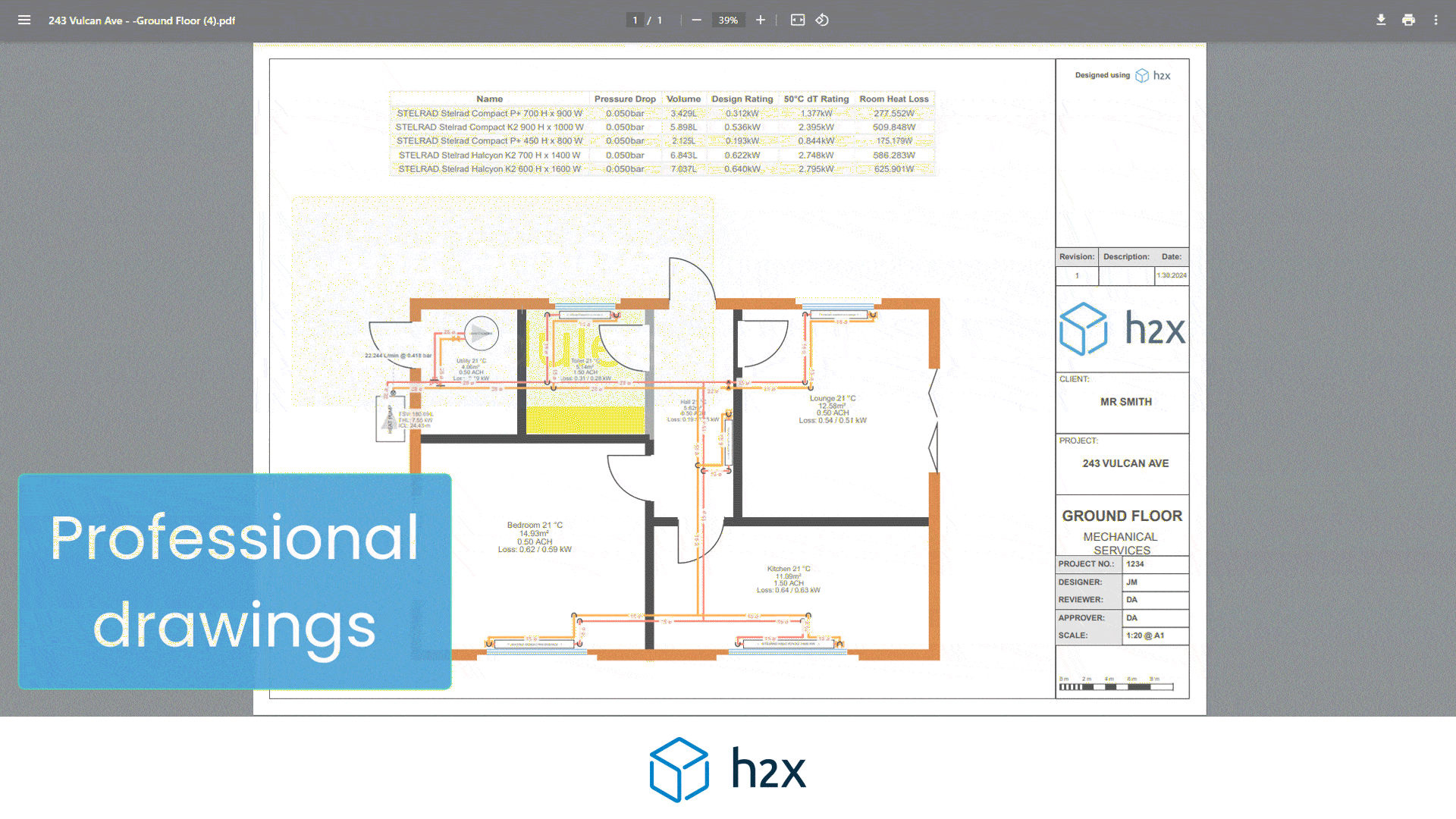
The head loss is calculated using the friction factor, which accounts for the resistance to flow caused by the pipe roughness of the interior surface.
The pressure drop in a pipe depends on several variables, including fluid density, fluid velocity, flow rate, pipe diameter (pipe d), pipe length (pipe l), pipe roughness, fluid viscosity, and acceleration due to gravity.
Find out how much water volume is in your pipe by simply inputting the pipe diameter (pipe d) and the pipe length (pipe l).
To accurately determine the pressure loss in a specific piping system, a calculation using fluid dynamics principles is required.
The friction factor (f) can be determined using several methods, such as the Moody diagram or the Colebrook equation, depending on the pipe roughness interior surface and the Reynolds number of the fluid flowing through the pipe.




 8615510865705
8615510865705 
 8615510865705
8615510865705