Radiant Heating & Cooling Systems - radiant heating system
Expansion tanks are divided into two compartments by a diaphragm or bladder. One part is for holding water that connects to the plumbing, and another section has air. In the event of heating, water undergoes expansion which is solved by an inflated partition in a tank of expansion which contracts to absorb increased pressure.
• Temperature: The expansion of water happens as it heats up. How much it expands depends on the initial and final temperatures of the water. Accurate temperature measurements are important when determining the amount of expansion.
Solution: Make sure you cross check your calculations and can explain how they work. Some examples of reliable sources to use are manufacturer catalogs for equipment volumes and verified tables for thermal expansion coefficients. Verify those results among your colleagues and see if they match up with industry standards.
Incorrect pressure settings may render the expansion tank ineffective or cause its premature failure either way. This is mainly because there is no proper understanding on what makes up the system pressure needs nor was there accurate initial pressure setting given.
radiantheat中文
• Cost-Effectiveness: Preserving integrity saves costly frequent repairs or maintenance which then reduces operating costs.
Solution: Take great care to study all manufacturer’s instructions concerning installation procedures. It must be located where it will allow control system pressure change properly. The firmness of joints and support systems should also be checked too.
Radiantfloor heatingsystemselectric
• Diaphragm or Bladder Tanks: They have flexible membrane or bladder which divides water from air; these are commonly used in residential homes and commercial facilities where heat is needed.
With these points in mind, you will be able to choose an expansion tank that is right for your furnace and use it safely and effectively. Visit our Step-by-Step Guide to Expansion Tank Sizing for a systematic approach on how to size an expansion tank.
Hot waterradiantfloor heatingsystems
Solution: Determine correct values for pressures based on what the system demands are like Atmospheric Pressure being 14.7 psi; then add operating pressure within that range desired by this mechanism used. Finally, ensure the pre charge pressure of the tank is in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations.
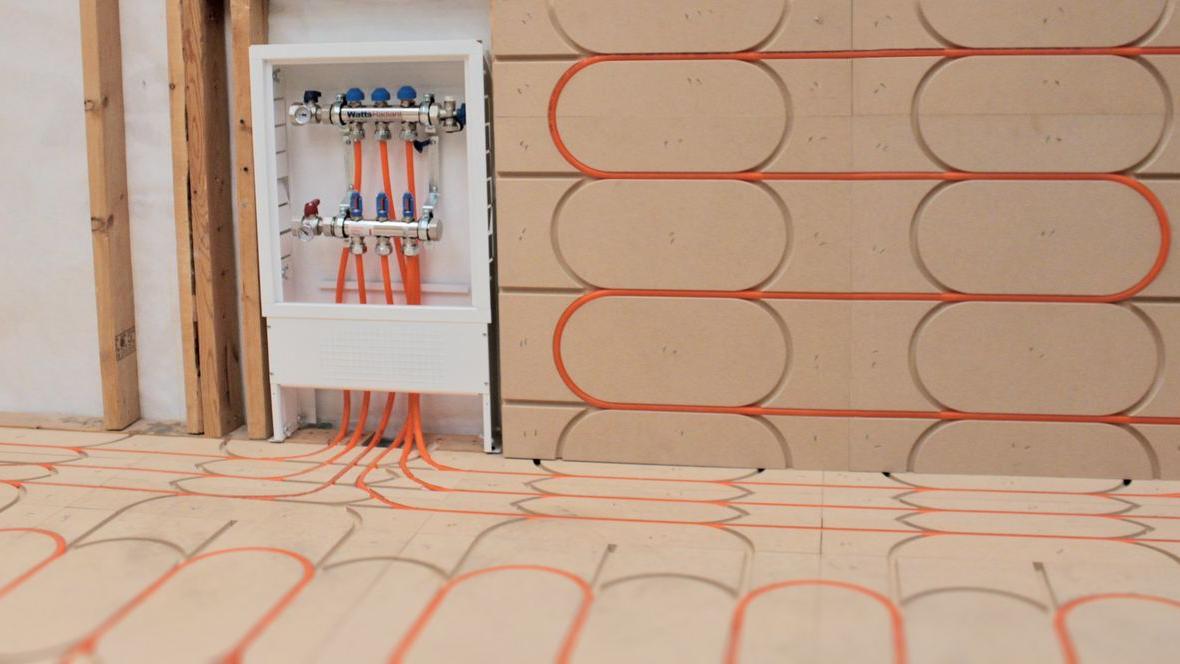
Since most radiant floor heating zones can be heated using low water temperatures, we are able to maximize energy savings by taking advantage of modern high efficiency boilers and water heaters as well as heat pumps. New control technologies allow the system to run at the lowest water temperatures required to heat the zones. This will greatly reduce energy loss as well as increase thermal comfort.
• Efficiency: It is possible to increase heating system performance and durability by ensuring it operates within appropriate pressure range.
What isradiant heatin a house
Improper installation such as incorrect positioning of the tank, improper pipe connections, not considering changes in system pressure might occur even if the calculations are done correctly.
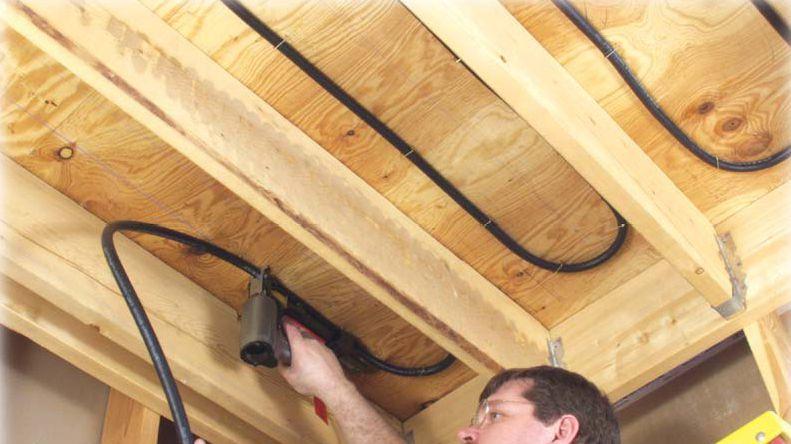
Hydronic Floor Heating is one of the most desired heating methods used today. It works by running warm water through tubing installed in the floor. The heat conducts from the water through the tubing and into the flooring system. Hydronic floor heating is very versatile. It can be installed in concrete slabs, under subfloors, on top of subfloor in thin slabs and sleepers. We usually can find a way to install a heating system into any floor. Since you are heating the entire floor there are no cold spots due to furniture. Room design is not affected by radiant floors.
Hydronic floor heating is excellent for commercial applications. Warehouses with high ceilings can keep the heat down near the floor where it's needed. Shops with large doors that open to let vehicles or material in/out can keep the heat in because it's stored in the mass of the building, not the air. When the doors open, the air will cool off, but as soon as the doors close the recovery is quick due to the large heat mass. Commercial applications also benefit from heated floors since occupants feel comfortable at lower air temperatures than systems that rely on heated air. When a mechanic is standing/sitting/lying on a heated floor, he feels more comfortable at 60-65 F air temperatures than a shop heated to 70F by forced air.
Radiant heatboiler
Understanding the basic principles of expansion tank sizing is vital in order to achieve safe and efficient heating and cooling systems. Consequently, this paper aims at highlighting various types of expansion tanks, the significance of temperature and pressure as well as precise calculations required herein.

The volume of water in the whole heating system determines how much water expands due to heat making it possible to determine volume for a suitable heater. Be large enough so that it could expand without increasing the amount of pressure in a given direction beyond certain limits. Calculated with respect to total water volume in a given system, water’s expansion ratio amongst others and some desired range of operating pressures.
Radiantheating system In ceiling
Solution: Include accurate temperature values for both low and high temperatures when calculating. For example, a system might have a chilled water supply at 44°F while outside temperature rises to 106°F

Maintenance of efficiency and safety of a range of heating and cooling systems largely depend on expansion tanks Sizing, which can be defined as units aimed at absorbing excessive pressure when water warms up and takes up more space. Lack of an expansion tank means that the rising pressure within the system could result in severe damage, costly repairs, and even dangerous situations.
This information aims to highlight the importance of capturing these factors and making accurate calculations because they determine the exact size of an expansion tank. Next, we explore fundamental science behind expansion tank sizing, procedural explanation on how to size the expansion tanks, typical hurdles experienced when sizing an expansion tank, and finally some helpful insights that can be used during this process.
Pressure is another significant determinant of the size of an expansion tank. As soon as it is controlled, pressure within the heating system will prevent injury to components and a proper functioning. The provision of space for water that has expanded by the expansion tank helps in controlling this pressure since prevents unnecessary high stress. A pre-charge pressure equivalent to the static pressure existing in the system is required for efficient operation of an expansion tank.
Best hydronicradiantfloor heatingsystems
Lastly, people love the feeling of a floor heating. If you are a contractor make sure you recommend adding floor heating to your customers project. They don't show off your hard work on their fin-tube radiator installs but they will rave about the radiant floor you put in. If you are a home owner, turn your house from a house that you like to a home that you love by adding radiant floor heating to it.
In closed water heating systems, expansion tanks are very crucial since they enable the system to work effectively and safely. For this reason, sizing of an expansion tank is important to enable it accommodate changes in water volume brought about by temperature variations. Below are some of the core principles that dictate how an expansion tank should be sized.
Solution: Always consult these correct tables when it comes to thermal expansion coefficients of materials that you are using. For instance, when working with carbon steel pipes, see to it that this value is calculated on specific values just for carbon steel usually about 6.5 x 10^-6 per degree Fahrenheit.
• Hydronic expansion tanks: These are designed specifically for hydronic heating systems that comprise the use of water as a medium through which heat is passed.
• Compression tanks: The type does not contain diaphragm or bladder but relies on an air cushion at its top part for expanding water; such tanks are mostly found in old systems.
I hope this manual has been useful in comprehending the subtleties of size expansion tanks. In case you have any issues or remarks, do not hesitate to contact us. Your response will be of great help in enhancing our services and giving more informative materials
An example is the incorrect calculations which are a familiar problem in sizing expansion tanks. Misinterpreting basic concepts or making errors in input data can generate such miscalculations as underestimating the volume of water in the system or using wrong thermal expansion coefficient for the pipe material.
Hydronicradiant heat
One key determinant of an expansion tank’s capacity is its temperature. When heated, water expands while upon cooling, it contracts. Conversely, if these actions take place without due diligence, this may endanger the whole system through high pressures. The additional space created after removing water from the system which enables stable pressure levels is filled up by the expansion tank.
Sometimes an error in selecting materials may cause inefficiencies or even failure of the tank assembly. The various materials have different coefficients of thermal expansions, using a wrong coefficient will make you end up with an over/undersized tank.
If you do not consider the right temperatures, then chances are that you will have an over/undersized tank. Volume of water changes along with the temperature and if the wrong numbers are used then errors occur.
• Pressure: Expansion tank size is influenced by system pressure. Higher pressures need greater tanks in order to hold higher volumes of expanding liquids. Calculations have to account for initial pressure (P1) and maximum allowable pressure (P2).




 8615510865705
8615510865705 
 8615510865705
8615510865705